(L217) Compound Conjunction Sentence Builders: “But”
$5.99 including GST
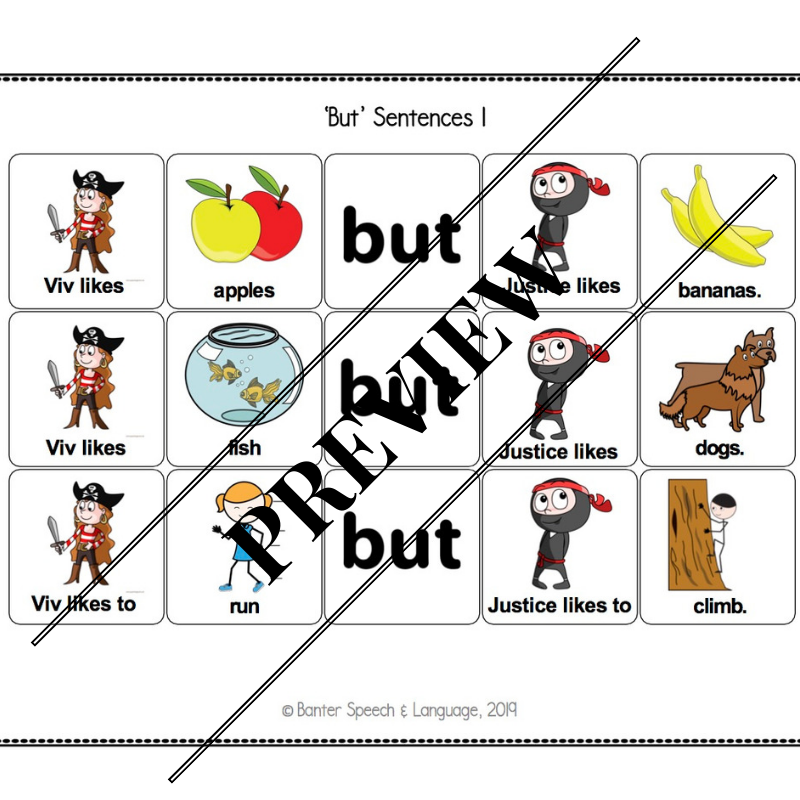
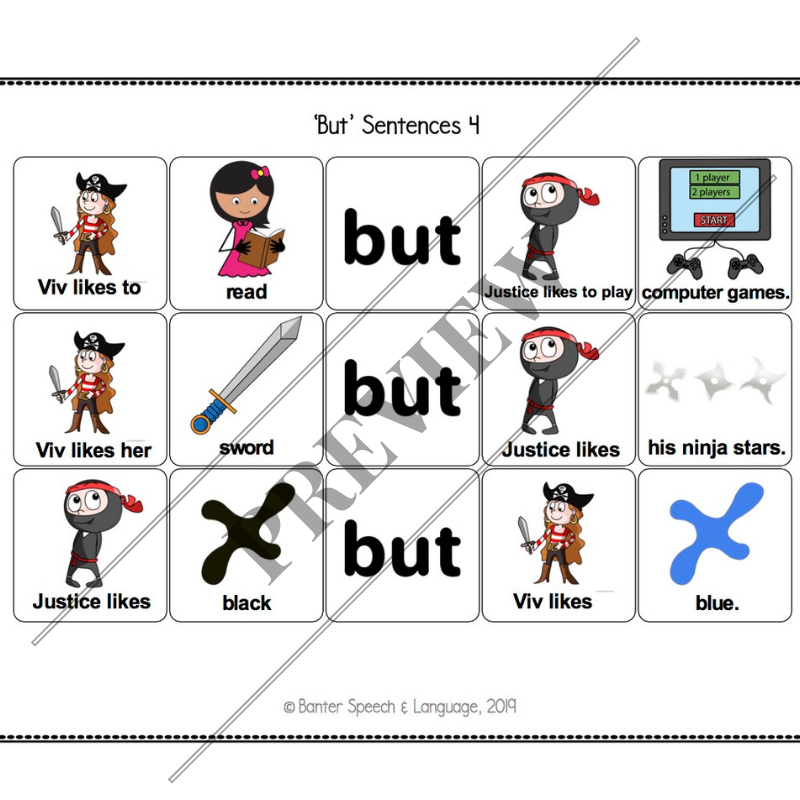
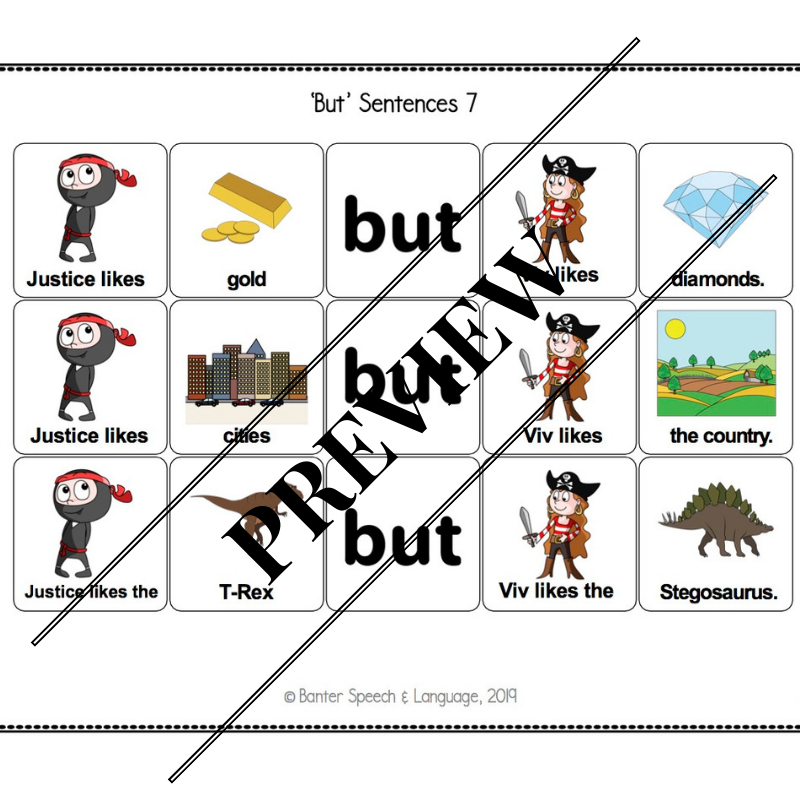
At around 3 years of age, typically developing children start to understand sentences containing the conjunction “but”.
In this 18-page no-prep pack, we introduce two friends who like different things. In addition to helping children to understand and to produce “but” sentences, this pack also promotes theory of mind development, starting with the fundamental idea that different people like different things.
Finally, basic categories (e.g. fruits, vegetables, actions) are used to stimulate semantic language development.
Description
At around 3 years of age, typically developing children start to understand sentences containing the conjunction “but”. “But” is a compound conjunction used to link ideas by showing contrast. For example, “I like to watch movies but my sister prefers to read books”.
Understanding “but” in sentences helps to build receptive and expressive oral language skills at the sentence level. It helps build the foundation to introduce more complex contrastive conjunctions like “although” and “even though”.
In this 18-page no-prep pack, we introduce two friends who like different things. In addition to helping children to understand and to produce “but” sentences, this pack also promotes theory of mind development, starting with the fundamental idea that different people like different things. Finally, basic categories (e.g. fruits, vegetables, actions) are used to stimulate semantic language development.
Tip: For people with significant communication disorders and people who are beginning to learn English as a second language, use a blank piece of paper to cover upcoming exercises to isolate one sentence at a time.