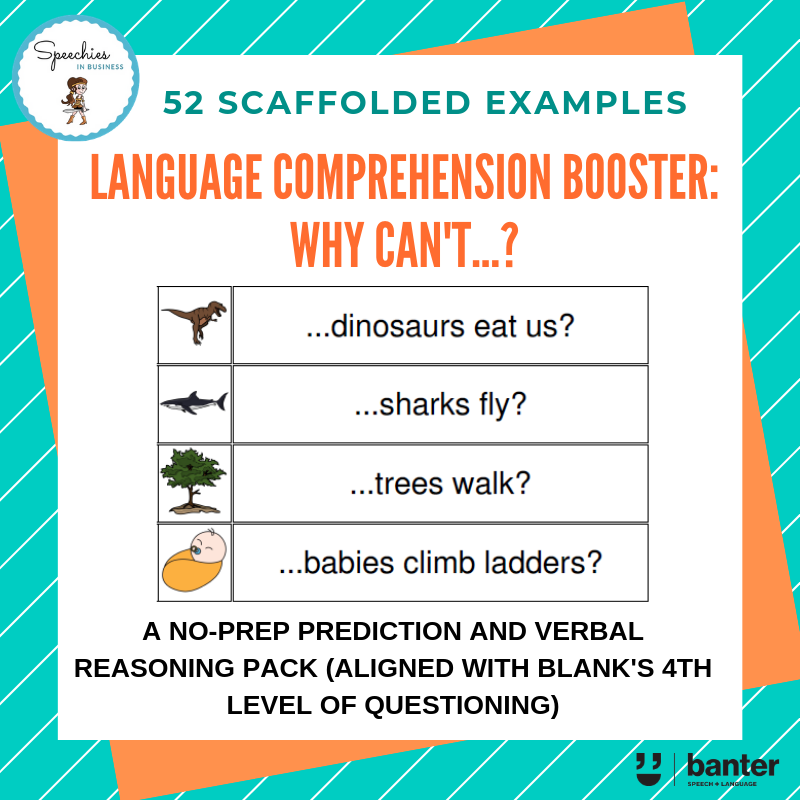
(L408) Blanks 4: Language comprehension booster: Why can’t?
$5.99 including GST
In this 17-page no-prep pack, we target Blank’s Level 4 language comprehension tasks. Specifically, we ask students to think about and explain why certain things can’t happen.
This requires students to generate mental models of each scenario, to reflect on their existing knowledge of the world, and to then explain why the subject can’t do the action required, e.g. by reference to an attribute like function, parts, or location.
This can be used as an oral language task, or as a written task. Negative questions are often very difficult for students learning English as a second language, and students with language or other learning disorders.
Description
Some researchers think that up to 15% of young school kids don’t have the language comprehension skills to cope fully with the demands of school (Hart & Fielding-Barnsley, 2009). Many of these kids struggle – some for their whole lives.
For most kids, school and home life plays a big role in helping to understand and use language (Morgan & Goldstein, 2004; Nation, 2005). So what can we do to improve students’ understanding of language?
Well, it helps to have a plan. And good plans are based on tried and tested frameworks. For language comprehension, one of the most influential frameworks was developed by Dr Marion Blank, a developmental psychologist. Dr Blank proposed four levels of abstraction, from least to most abstract:
- Level 1: Directly supplied information (Matching perception).
- Level 2: Classification.
- Level 3: Reorganisation.
- Level 4: Abstraction and Inferences.
Many Level 3 and 4 tasks require children to make inferences – ideally skills we want kids to have or to be developing when they start school and start learning to read.
Most (although not all) kids start school with an ability to complete Level 1 and 2 tasks. But from there, it gets rocky: about 50%-65% of 5 year-old kids from well off households with educated parents can answer Level 3 questions – but only about 10% from disadvantaged backgrounds, including kids with average intelligence. Many children with Autism Spectrum Disorder or social language disorders have significant difficulties answering Level 3 and 4 questions.
In this 17-page no-prep pack, we target Blank’s Level 4 language comprehension tasks. Specifically, we ask students to think about and explain why certain things can’t happen. This requires students to generate mental models of each scenario, to reflect on their existing knowledge of the world, and to then explain why the subject can’t do the action required, e.g. by reference to an attribute like function, parts, or location. This can be used as an oral language task, or as a written task. Negative questions are often very difficult for students learning English as a second language, and students with language or other learning disorders. This pack is designed to give students lots of practice at understanding negative questions and to explaining why subjects can’t perform given actions.